
International Relations 1920-1945
The Aftermath of WW1
-
Following World War 1 when the treaty of versailles was signed Germany had to take the blame for starting the war. This is known as war guilt
-
They had to pay reparations to other countries for deaths caused. The german people were outraged by this as it was their leaders not they who started the war
-
The German army and navy was greatly downsized
-
The German economy declined rapidly and people became poorer and poorer
-
Germany also had to give back any land it had gained during the war such as the Rhineland between France and Germany


Right: Germany following WW1. Severe destruction led to thousands being homeless
Left: The Treaty of Versailles was a declaration of Germanys surrender and was despised by Hitler
The League of Nations:
-
The leaders of Versailles decided it was necessary to start an organisation to prevent wasr from breaking out again
-
All countries were expected to join. Its headquarters was located in Geneva, Switzerland. If any country invaded another the league would isolate and punish that country with sanctions. These sanctions would block their exports
-
However there were problems. The league had no army to back up its decisions and the two biggest world powers, America and Russia, did not join
Italy after WW1:
-
Italians were upset following the war as they had lost territory, there was high unemployment and huge inflation
-
Benito Mussolini started the fascist party and promised to make Italy great again
-
He surrounded himself with bodygaurds called blackshirts and travelled to meetings with this group and attacked anyone who disagreed with Mussolini
-
He also promised Italiens that if they voted for him he would make Italy an important and respected place again
-
Later his fascist party marched to Rome to demand power from the king. The king was frightened of Mussolini's power and allowed him to become Prime Minister
-
In power Mussolini abolished all other political parties
-
He closed down newspaers who did not agree with his views (Censorship)
-
He introduced propaganda, which consisted of pictures of himself everywhere to make him seem powerful
-
Economically he delivered huge employment opportunities by starting a motorway construction project of Autostrada
-
Also he drained huge malaria filled marshland known as the Pontine Marsh. Following this he planted wheat to provide bread and pasta for Italians
-
These added to his popularity and those who didn't agree with his policies were killed or jailed


Left: Benito Mussolini was actually a small man but used pictures to make himself look taller
Right: Mussolini and his blackshirts marching to Rome to demand power from King Victor Emmanuel III of Italy
Mussolini's Foreign Policy
-
Mussolini wanted Italy to have a big Empire to make his country great again so he sent hi troops into Absynnia (Modern day Ethiopia)
-
The League of Nations ordered Italy to withdraw- Mussolini igonored the league and instead signed a treaty with Hitler known as the Rome-Berlin axis in which they promised to help one another if attacked
Hitlers coming to power:
-
Germany after WW1 was a place of high unemployment, inflation and people who had a sense of great unfairness at how ordinary germans were made pay the reparations
-
Adolf Hitler (Austrian) exploited these feelings and like Mussolini promised to make Germany great again
-
Joined and lead the Nazi party with a private bodygaurd. S.A- Brownshirts and the S.S
-
They got rid of any opposition the Nazi party became more and more powerful
-
However after a falied uprising Hitler was sent to prison where he wrote "Mein Kampf" or "My Struggle"
-
In this book he set down his beliefs. He believed:
-
That all germans were a part of a master or aryian race
-
All "inferior" races especially the Jewish race should be exterminated
-
All German speaking people should be united in a new German Empire "Third Reich"
-
Germnay should expand into other countries for "Living Space" or "Lebansraum"
-
Hitler was later released from prison and in 1933 his nazi party became more popular and Hitler became Chancellor
-
All parties except the Nazi Party were abolished
-
Secret police (Gestapo) rounded up enemies
-
When the leader of the S.A criticised him, Hitler had all of the S.A rounded up and killed during The Night of the Long Knives
-
He used propaganda to show himself in a good light through posters and Radio-Broadcasting
-
All children had to join the hitler youth movement



Hitlers set down his radical beliefs in this book which has sold more than 5.2 million copies
Ernst Rohm was leader of Hitlers infamous S.A. He was one of the founding members of the Nazi party
Hitlers secret police, the S.S or Gestapo pictured with their leader Heinrich Himmler
Hitler and the Jewish Persecution
-
Hitler hated the jews and vowed to deprive them of their rights
-
He passed the Nurembourg Laws which deprived them of their citzenship and forced each one to wear a yellow star of david on their coats
-
The gestapo attacked and broke up jewish businesses on "Kristallnacht" or "The night of the broken glass"
-
Hitlers next step was to deport jews to work or concentration camps where most were killed by gasing. This is what Hitler called his "Final Solution" to the Jewish problem
-
6 million jews were killed in what became known as the "Holocaust". However jews were not the only group targeted by Hitler-Homosexuals, people with learning disabilities and gypsies were also killed

Auschwitz concentration camp in Poland is one of many of Hitlers concentration camps
How hitler entered the War
-
Hitler despised the Treaty of Versailles and wanted to destroy it. He also wanted to rebuid the German army and create a bigger Germany for his master race.
-
He stopped Germany paying reparations
-
He secretly rebuilt the army(built munition factories)
-
He sent troops into the Rhineland in 1935
-
He annexed Austria. This was known as Anschluss
-
At this stage Hitler was worrying the Uk and French Prime Ministers, however both were extremely afraid of another war breaking out they did nothing. This was known as appeasement
5. Hitler then took over a German speaking part of Czechoslovakia known as the Sudetan Land
-
The U.K and French prime ministers finally intervened and met with Hitler. During the meeting Hitler agreed to stop attacking. This was known as the Munich agreement
7. In September 1939 Hitler invaded Poland- War was then declared by the Allies on Germany for breaking their agreement.
Britain at War:
-
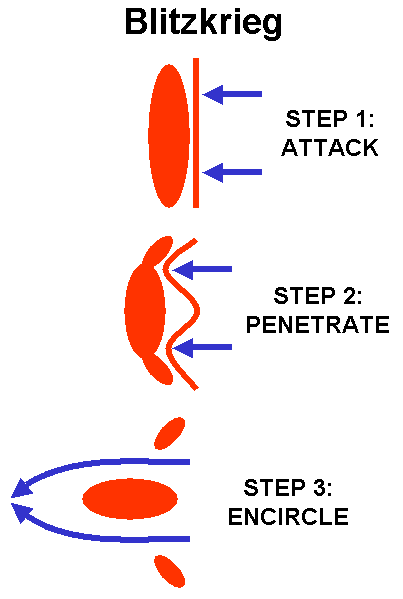
Blitzkreig was a new german tactic meaning lighting war. Using this tactic the Germans would firstly send in the airforce to bomb infrastructure, air fields and hospitals, they would then send in tanks to kill off any remaining soldiers and finally soldiers or infantry would be sent in to take control of the territory
-
In 1939 the Phoney War began. It was given this name as even though the allies were at war no fighting took place that winter
-
Norway and Denmark eventually were conquered by Hitler, followed by Holland, Belgium and France
-
Once France was conquered, Hitler turned his eyes to Britain in operation Sealion
-
First the German Airforce or the Luftwaffe were sent into destroy the R.A.F., his bombers attempted to bomb R.A.F planes while still on the ground. However the R.A.F. pilots fought off the Luftwaffe by taking double shifts and using radar. This became known as the "The Battle of Britain"
-
Hitler was forced to postpone his invasion of Britain. This was the first real defeat Hitler faced
-
He changed his policy to "Blanket Bombing" of the British cities in what became known as the Blitz
-
Submarines known as U-Boats tried to cut off all British supply lines and all imprted foodstuffs had to be rationed
-
Operation Barbossa now began, which was the invasion of Russia
-
Hitler sent in 3 million troops to russia with 10,000 tanks and split the force into three groups. Each one to Leningrad, Stalingrad and Moscow. Hitler was particularly interested in Stalingrad due to its large oil fields
-
However, the harsh Russian winter hindered their advancement as petrol froze in tanks and soldiers died of hypothermia
-
During the battle of Stalingrad the Germans surrounded the citybut the Russians fought back and managed to surround the German army and forced a surrender. Around 20 million people died during Operation Barbossa. This was Hitlers second largest set-back


Britsh Spitfires getting into formation during the Battle of Britain
A diagram explaining the steps involved in Blitzkreig
Russian or Soviet troops defending during the Battle of Stalingrad
Exam Tip: This part of the History course, like many other, is extremely long. I have broken it down as much as possible but i would advise you to learn only a section or two at most a day and use the pictures I have included to help your learning. Good Luck!
The U.S enter the war:
-
In the pacific Japan was conquering large parts of Asia
-
The Japenese airforce attacked the American fleet at Pearl harbour in the Pacific and as a result the U.S joined the war on the side of the Allies against Hitler
-
The american and allies combined forces and defeated the Germans in North Africa under General Montgomery
-
Both Armies then invaded Italy and defeated Mussolini
-
On the 6th of June 1944 a large force of americans and allied forces landed in Normandy, France to free France (D-Day)
-
A little later the allies captured Berlin where they encountered with Stalins red army, however they could not agree on what to do with territory. They eventually agreed to divide and all of Germany into East (Controlled by the Soviets) and West (controlled by the Allies) as a temporary measure, Germany officially surrendered on the 7th of May
-
In the Pacific war raged on. The japenese were continued to conquer large areas of Asia and refused to surrender despite being bombed
-
The Americans decided to use their new untested weapon, an atomic bomb, to force a Japenese surrender. 40,000 died instantly in the city of Hiroshima and Nagasaki and hundreds more dies later from radiation poisoning. The Japenese surrendered.
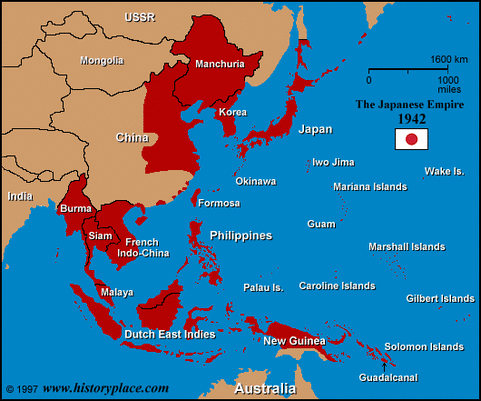


The extent of the land conquered by Japan during WW2 is highlighted in red
The city of Hiroshima following the dropping of an Atomic Bomb
General Montgomery or The Spartan General was credited with defeating Hitlers General Rommel (The Desert Fox)
The Results of WW1:
-
Around 50 million people died in WW2
-
Millions were left homeless as refugees
-
Leaders of France and Germany would come togther to form the E.E.C. which later became the E.U to prevent any more war breaking out
-
The economies of the European countries especially Germnay and France were destroyed