
Chapter 3: Respiration and Breathing System

-
Larynx (Voice Box): Used to make sound
-
Trachea: Connects the lung to the outside world
-
Rings of Cartilage: Strengthen th trachea
-
Right\Left Bronchus: Branches of the trachea
-
Bronchiole: Carries air throughout the lung
-
Alveoli: Air sacs where gaseous exchange takes place
-
Rib cage, inter-coastal muscles and diaphragm: All involved in the mechanism of taking a breath (i.e inhaling and exhaling)
-
Breathing is also known as external breathing
-
The function of the breathing system is to take in oxygen and to excrete carbon dioxide and water vapour
-
The lungs, bronchi, trachea, bronchiole and alveoli are vall parts of the breathing system
-
The diaphragm, the ribe cage and intercostal muscles are involved in the mechanism of taking a breath
-
Air enters the lungs when the diaphragm pulls down and the rib cage expands
Parts of The Breathing System
Notes on Breathing System
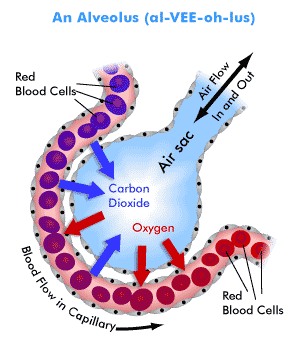
Gaseous Exchange in the alveoli
-
In the breathing system we take in oxygen and this enters the bloodstream through the alveoli
-
This blood circulates through the body and provides oxygen to the cells in the body
-
The blood containing oxygen is a bright red and unoxygenated blood is a more purple colour as you can see in the diagram
-
As the blood circulates through the body the oxygen is used up in cells and the cells then excrete carbon dioxide which enter the blood stream
-
This unoxygenated blood returns to the alveoli the carbon dioxide is removed and oxygen enters the blood and the cycle begins again
-
The carbon dioxide removed in the alveoli is then excreted by being exhaled
Difference in inhaled and exhaled air
Oxygen Carbon Dioxide
Inhaled air: 21% .03%
Exhaled air: 16% 4%
-
As you can see from the table above there is more carbon dioxide in exhaled air than inhaled air
-
This is due to the fact that the cells in the body take in oxygen from the blood and then excrete carbon dioxide in to the bloodstream
-
As a result the blood now contains less oxygen and more carbon dioxide and this is then excreted through the alveoli leading to this increase in carbon dioxide