
Chapter 8: The Reproductive System
-
A gamete is another name for a sex cell
-
Fertilisation occurs when a male gamete (sperm) and a female gamete (egg) combine to from a new cell called a zygote (a new cell)

Parts and Functions:
Part: Functions:
Testicle: Produces male hormone and gamete (sperm)
Scrotum: Holds the testicles outside the body to prevent damage from heat
Sperm Duct: Transports sperm from the testicles to the penis
Seminal Vesticle:
Prostate Gland These two parts produce the fluid that combines with sperm to produce semon
Penis: Delivers semon into the womans body
Female Reproductive System:
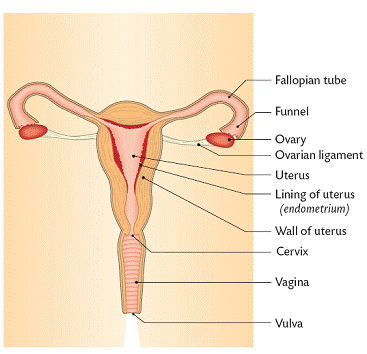
Parts and Functions:
Parts: Functions:
Vagina: Holds the penis during intercourse
Allows for childbirth
Cervis: Entrance to the womb
Uterus: Holds the baby during pregnancy
Fallopian Tube: Fertlisation takes place here
The egg is carried towards the womb throught this
Ovaries: Produces the female gamete (egg) and hormone
The Menstual Cycle:
-
The menstrual cycle lasts on average 28 days
-
Menstruation or a period occurs when the lining of the womb which was built up in expectation of childbirth falls away as no egg has been fertilised
-
Menopause is the time in a womans life when menstruation no longer occurs
-
The fertile period is day 11-17. This is the period in which a woman can become pregnant. An egg can last for 2 days and sperm can last for three
Day 1-5: Menstruation/Period occurs
Day 6-13: The lining of the womb begins to build up
Day 14: Ovulation- When an egg is released from the ovaries
Day 15-28: The Lining of the uterus stays in place and the egg dies on day 16
The Menstrual Cycle (28 days)

Stages of the Menstrual Cycle (you do not need to learn this)
Stages of Fertilisation:
-
A man places his penis in the womens vagina and ejaculation takes place (the release of semon)
-
The sperm swim up into the fallopian tube where it combines with the egg and fertilisation takes place
-
Successful fertilisation can only take place in the fallopian tube
-
The fertilised egg then implants itself in the lining of the womb. The woman is now pregnant
Contraception:
-
Contraception is the prevention of fertilisation
-
This can be done in many ways using for example a condom or a contraceptive pill
Part and functions of the zygotes protection:
Part: Function:
Placenta: 1. Reomoves waste from the foetus' blood into mothers blood for excretion
2. Filters oxygen and nutrients from the mothers blood to the foetus
Umilical Cord: Connects the placenta to the foetus
Amniotic Fluid: Cushions the baby
Amnion: Holds the amniotic fluid in place
Notes on Pregnancy:
-
During the period of pregnancy the zygote or new cell develops into the foetus (a developing child) which is supplied by the placenta
-
The time between contraception and birth last up to 40 weeks
-
During pregnancy the baby's head is facing down and the mother goes into labour
-
The wall of the womb or uterus contracts in spasms.
-
The amion burst realeasing the amniotic fluid (water breaking)
-
The baby is born head first and the umbilical cord is cut
-
The rest of the umbilical cord and placenta pass out later (afterbirth)
Puberty in Boys:
Puberty in Girls:

-
Shoulders widen, chest deepens and increase in muscles
-
Penis and testicles increase in size
-
Pubic hair appears-facial hair and other hair
-
Increased interest in girls
-
Increase in Height
-
Testicles begin to produce sperm and semon
-
The larynx widens causing a voice break and the a deepening of the voice
-
Spots may begin to appear
-
Ovaries and womb increase in size
-
Increased interest in boys
-
Spots may appear
-
Breasts increase in size
-
Hair may begin to appear
-
Increase in height
-
Hips widen
-
The menstrual cycle begins
Puberty is the time in a persons life when they become sexually mature
Genetics:
-
Genetics is the study of hereditary
-
Inheritable charecteristics are charecteristics we inherit from our parents e,g hair colour, eye colour etc. These charecteristics are decided by our genes
-
Non-inheritable charecteristics are charecteristics that are learned e.g horse riding, playing a musical instrument etc. We also develop certain charecteristics from our environment, for example if both your parents speak Spanish you too will speak spanish from a young age
-
Chromosomes consist of a D.N.A molecule wrapped around protein which is found in the nucleus. This then contains the genes
-
The gene is found along the length of the chromosome-A small section of D.N.A
-
Human cells have 46 chromosomes -in 23 pairs except for the gamete which has only 23 gametes